Explore Our Programs
Quick Links
Events

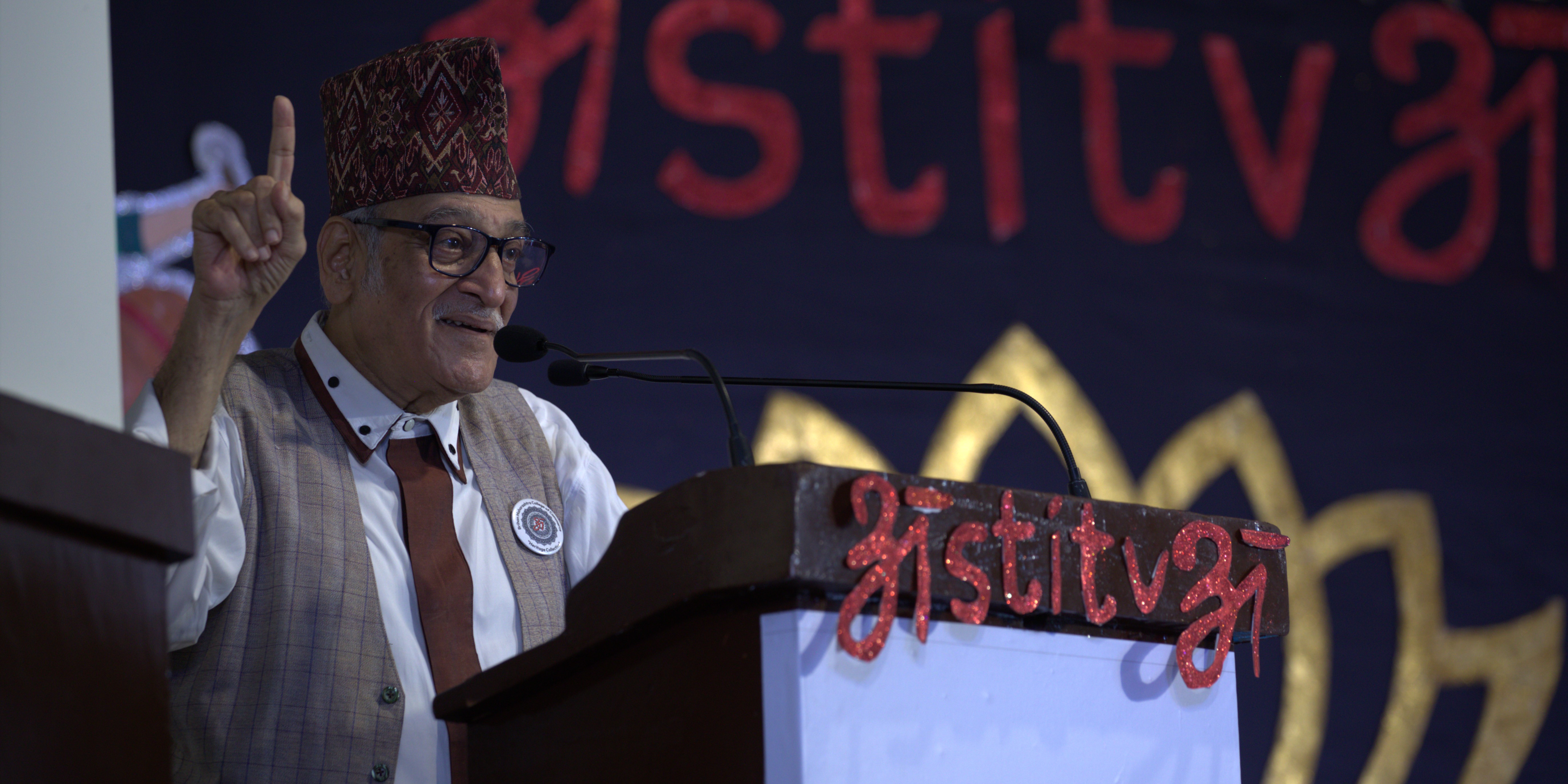
ASTITVA
Astitva 2022 organized by Heritage Collective was indeed a blockbuster event this year.

NATURE CLUB
Plantation is the most important in this todays world. Save earth
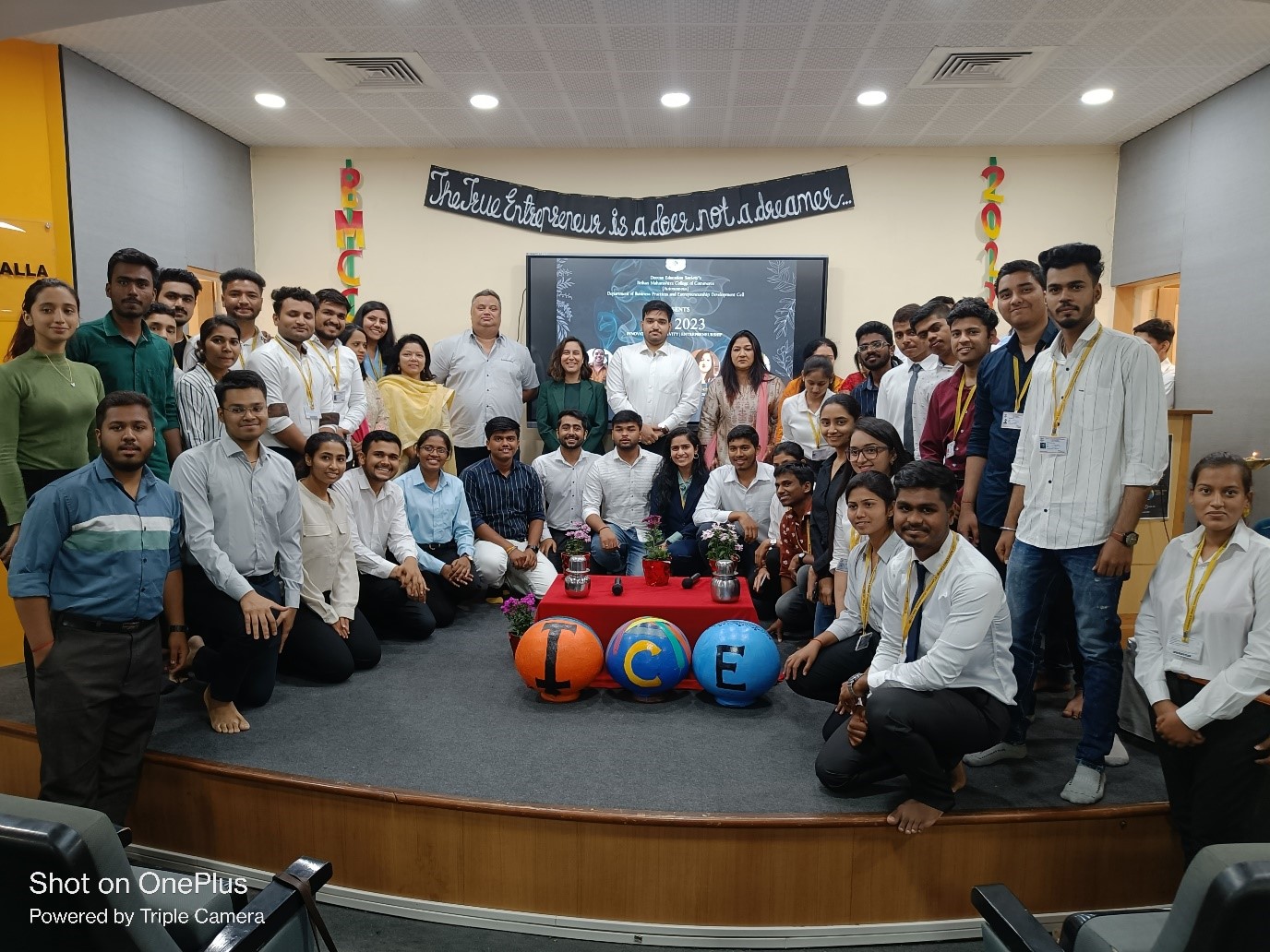

INNOVATION CREATIVITY AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP
The Brihan Maharashtra
College of Commerce,
through its Business Practices

PATRIOTIC EVENTS
Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav! 75 Years of Independence!
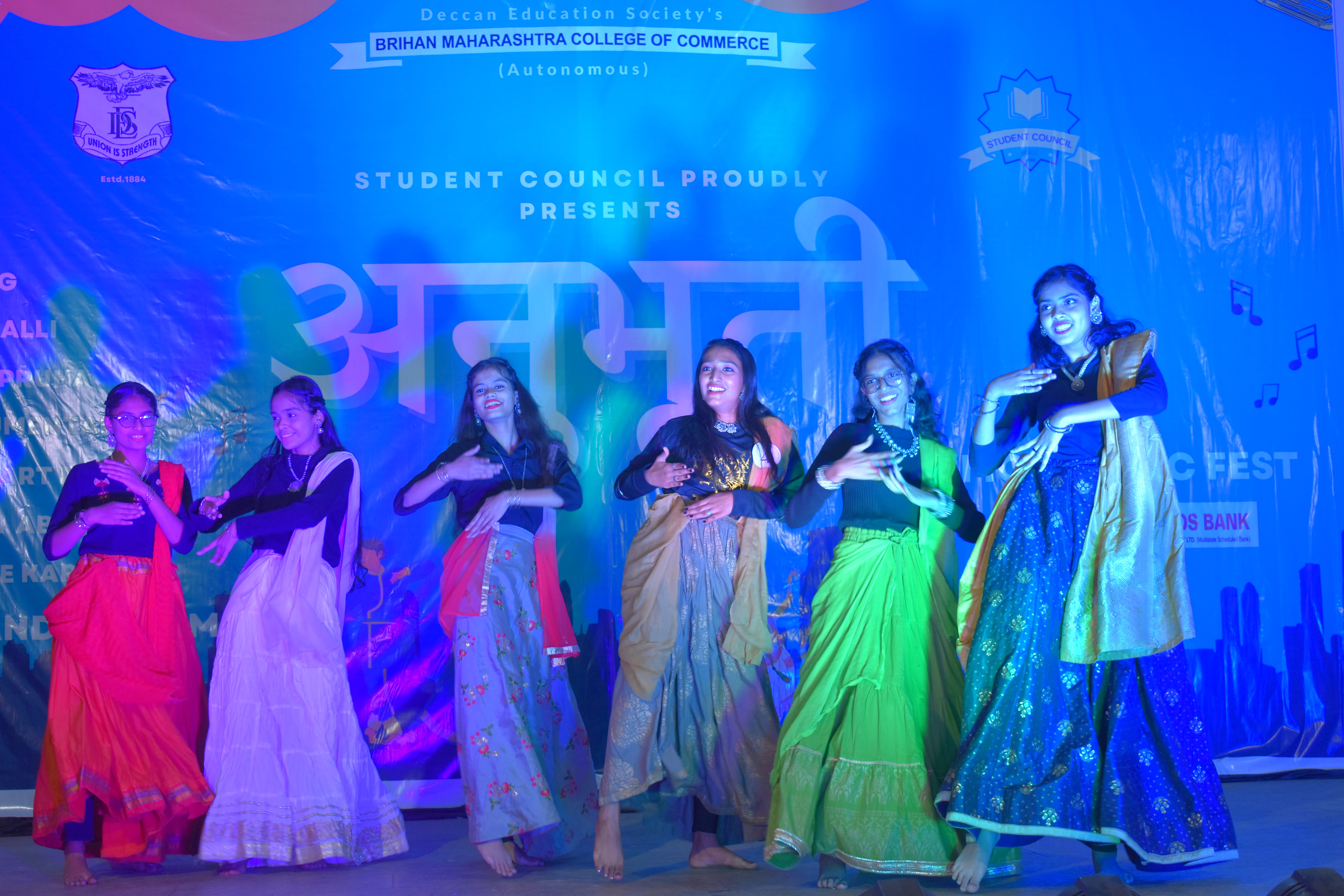

Annual Social Gathering
Anubhuti

MOOTCOURT
mootcourt
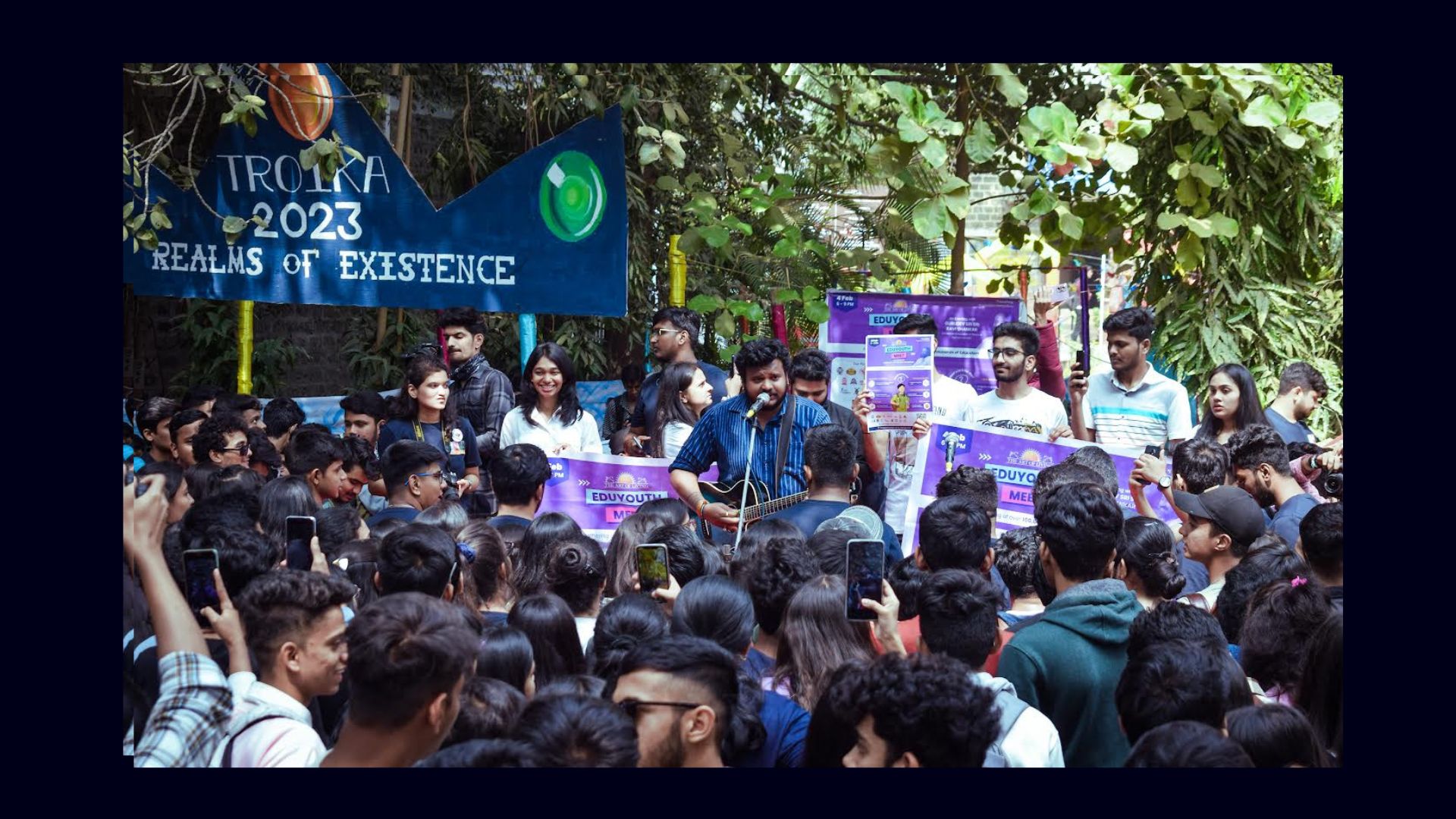

TROIKA
Troika means merging of three different activities.
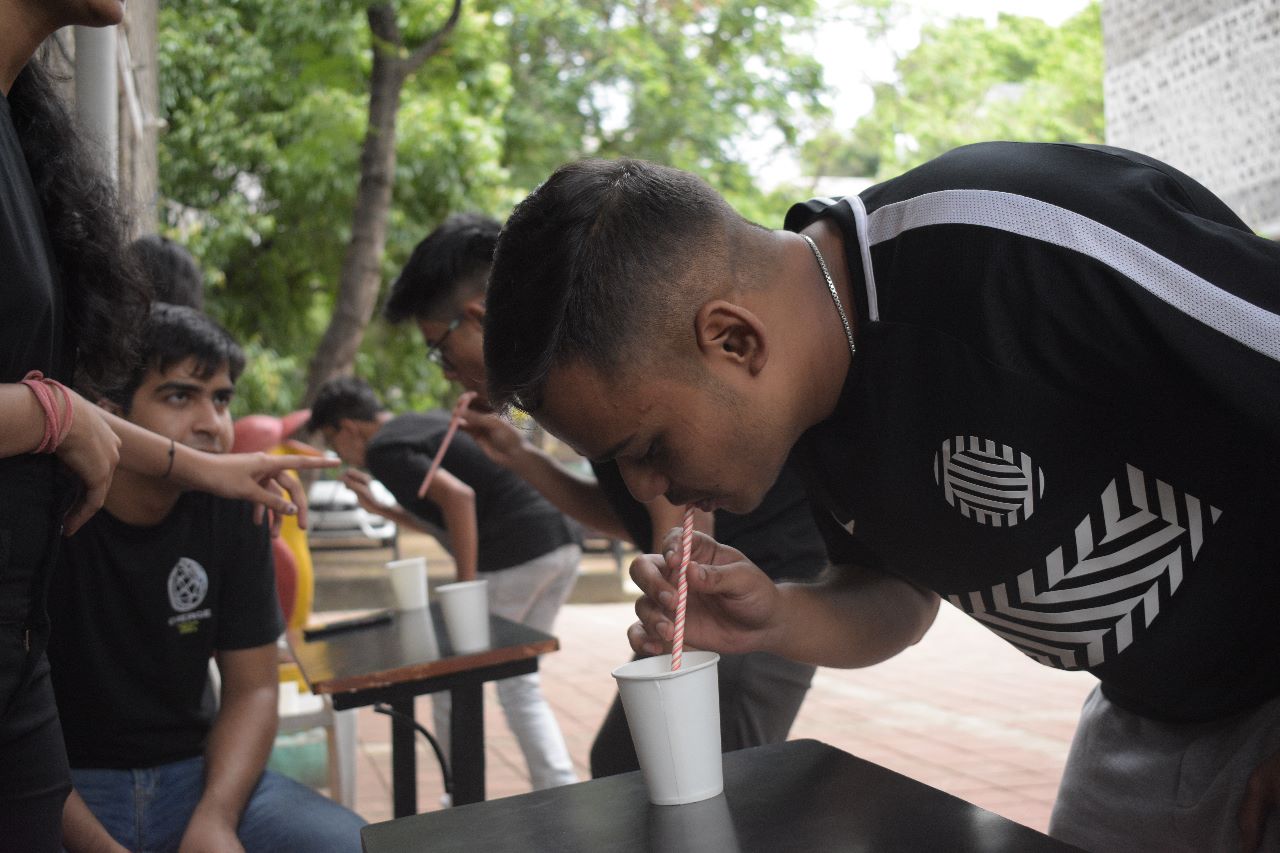

E-merge
"EMERGE 2022-23: Unleashing Talent, Igniting Innovation!"

Red Cross
red Cross
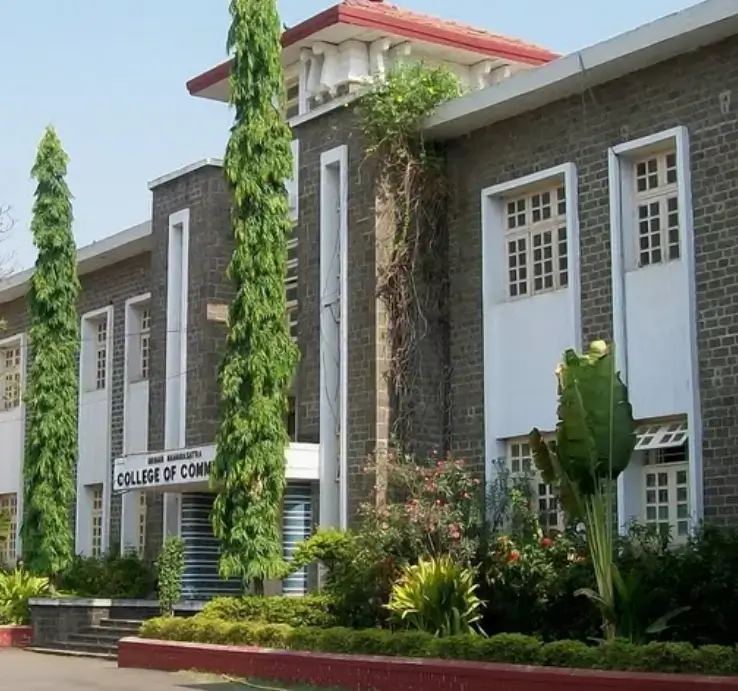
About BMCC
The Brihan Maharashtra College of Commerce (BMCC) is a pioneering, premier degree commerce college in India, situated in the city of Pune, Maharashtra. The College was established in 1943 by the Deccan Education Society with a view to providing enlightened leadership and trained manpower in the field of commerce

The Brihan Maharashtra College of Commerce (BMCC) is a pioneering, premier degree commerce college in India, situated in the city of Pune, Maharashtra. The College was established in 1943 by the Deccan Education Society with a view to providing enlightened leadership and trained manpower in the field of commerce and
 office.bmcc@despune.org
office.bmcc@despune.org +91 20 6765 6200
+91 20 6765 6200